THE QUICK GUIDE TO VERTICAL TURBINE PUMPS
Vertical turbine pumps are mostly used to pump water from deep pits or wells to some sort of water distribution system. In this post, we’ll discuss how they work, what they’re great for, advantages, and disadvantages of use so you can get a better understanding of this unique type of centrifugal pump.
VERTICAL TURBINE CHARACTERISTICS
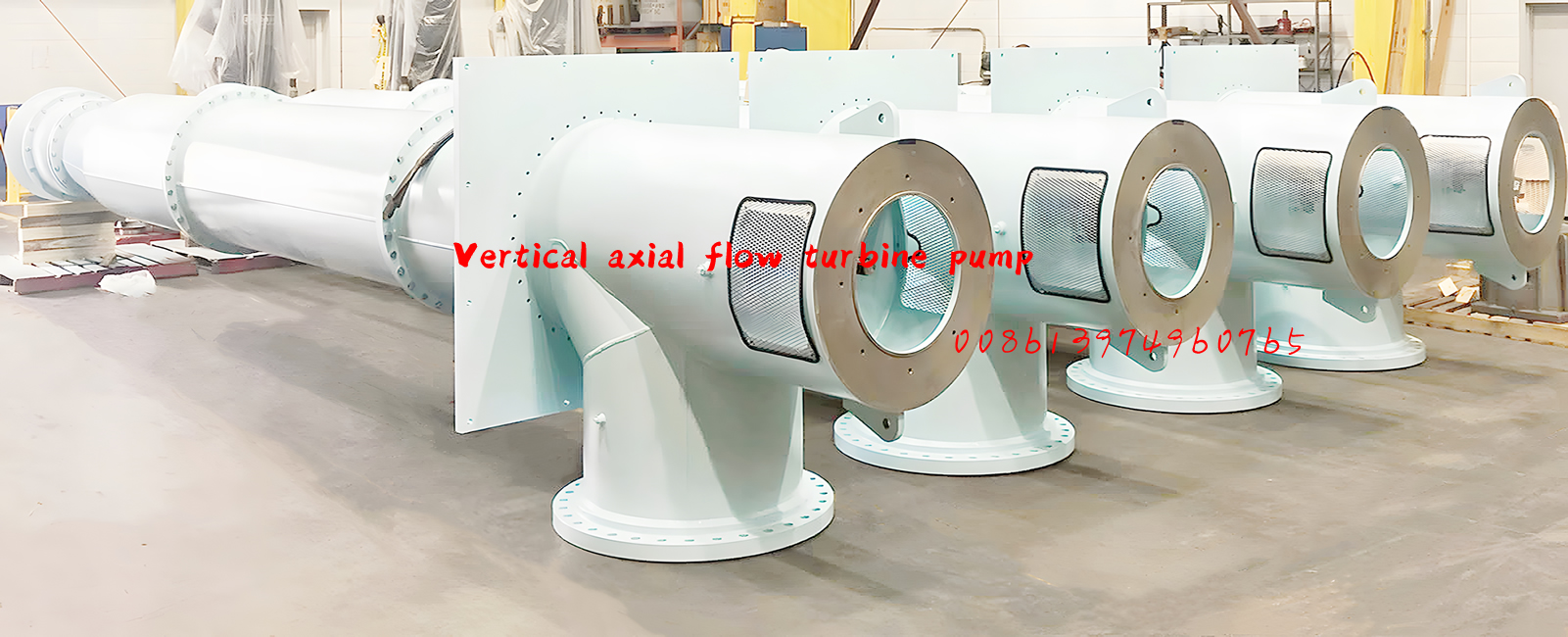
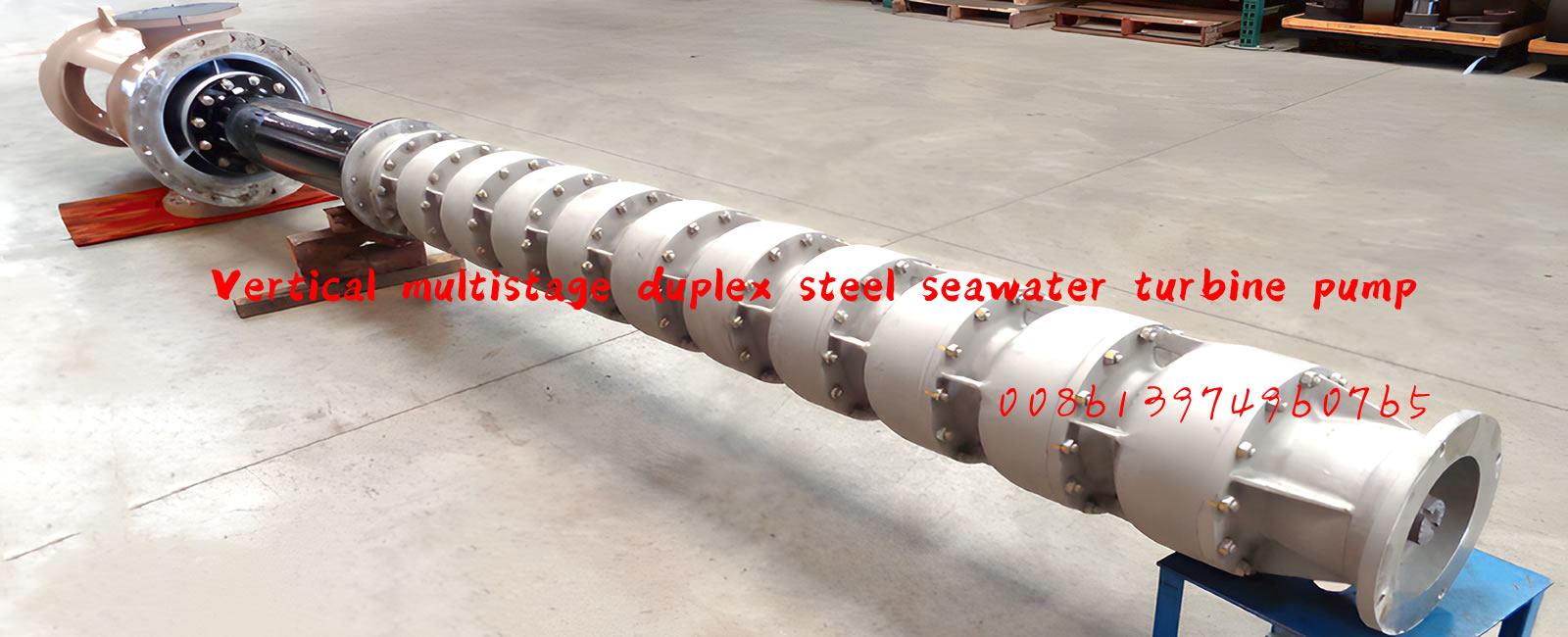
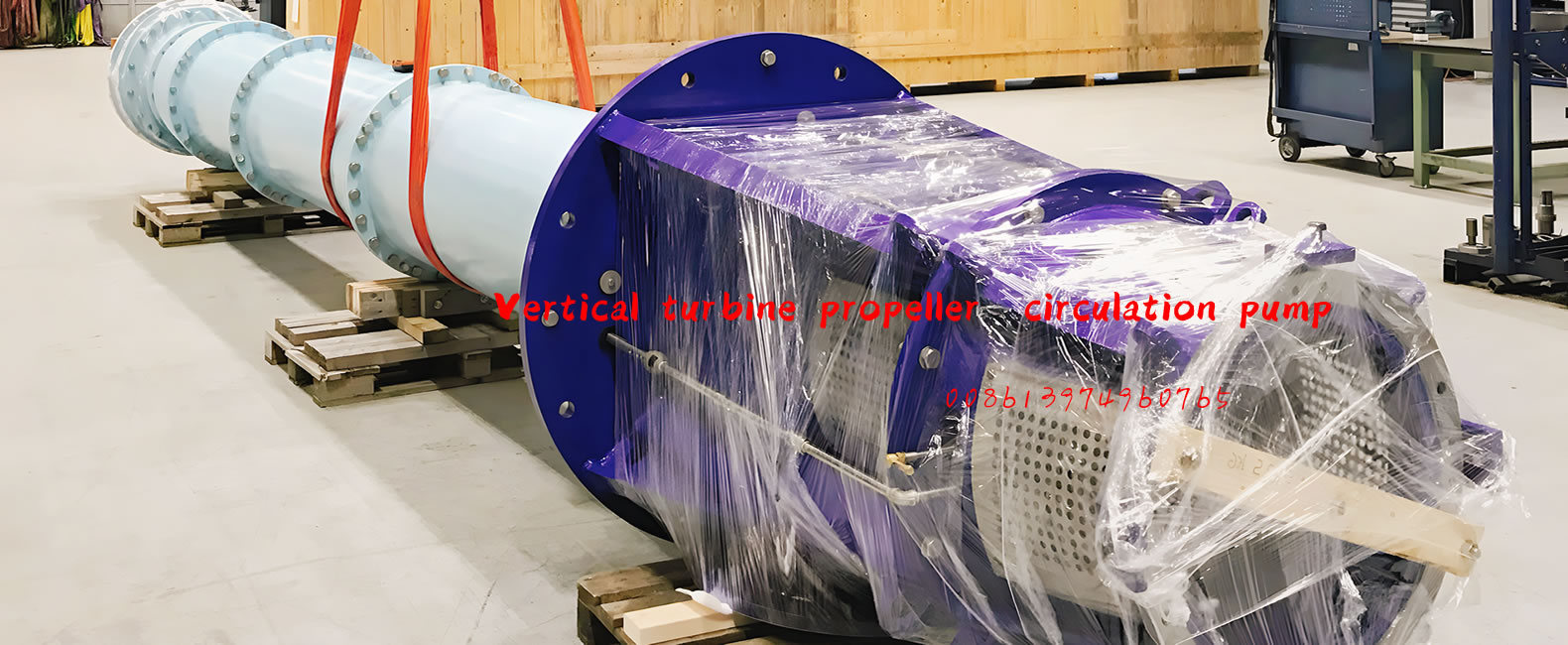
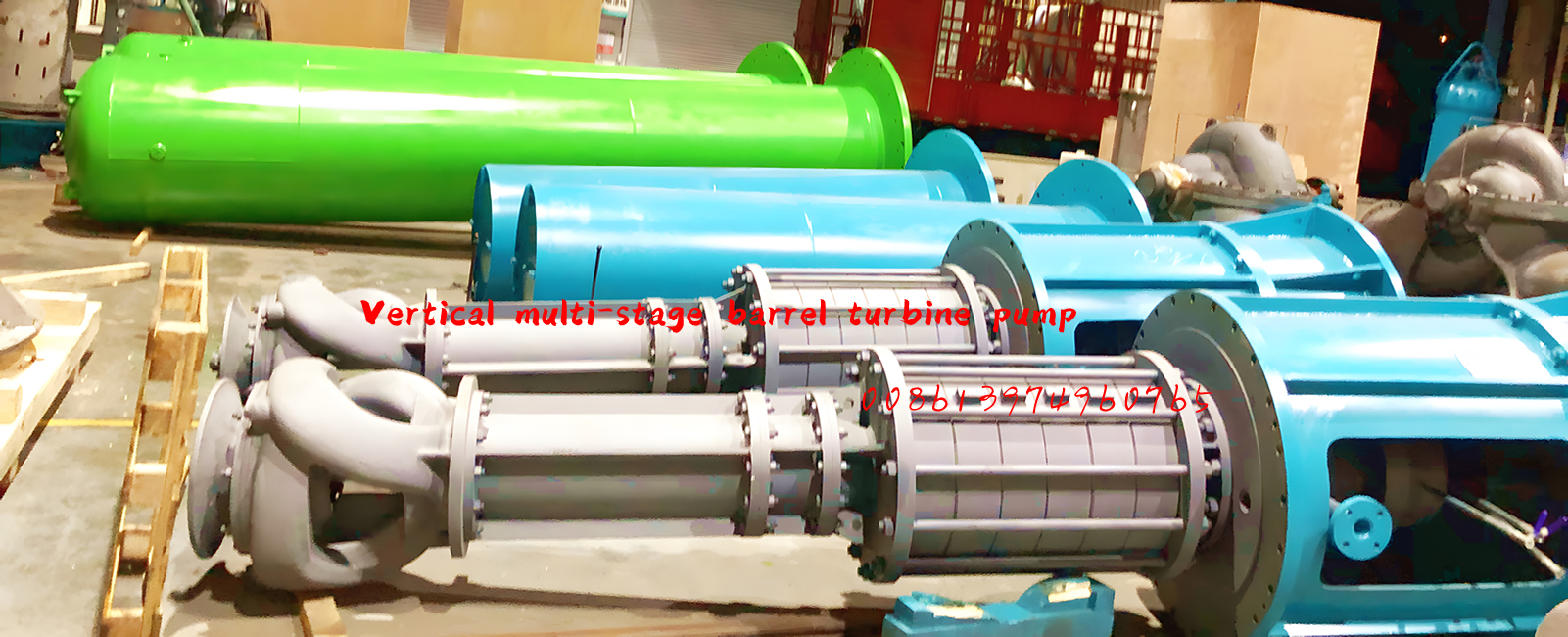
Vertical turbine pumps are comprised of a motor, discharge head, one or more flanged columns to house the shaft, and one or more bowls (or stages). It’s also recommended that a basket strainer is installed on the last bowl to prevent large solids from entering the pump.
BEST APPLICATIONS
Vertical turbine pumps can be found in a wide range of agricultural, municipal, and industrial applications. They are generally meant for clean water applications that require high pressure and high head. They are most commonly used to pump out of deep pits or wells.
ADVANTAGES
Vertical turbine pumps have a small footprint, and there are no priming issues (as long as minimum submergence requirements are met) due to the impellers being submerged in fluid. They are easily customized, and are highly efficient on high head, low flow applications.
DISADVANTAGES
Large amounts of headroom are required for installation and maintenance. Hydraulic thrust is difficult to balance on vertical turbine pumps due to their overhang design, especially in high suction, high pressure applications.
This type of pump can also experience issues with mechanical seals when pumping fluids with entrained or dissolved gas. The gas tends to accumulate at the top of the stuffing box or seal chamber, where venting is difficult.
If you're experiencing issues with a vertical turbine, talk to an engineer experienced in troubleshooting these types of pumps. Doing so will help your pump perform at its highest efficiency.


























 QQ
QQ